Modelling a heat exchanger by CFD
A heat exchanger is equipment used to transfer heat from one fluid to another. Either the purpose is to recover heat from an off gas system to preheat another gas, either cooling is envisaged by a refrigerant. The heat transfer efficiency depends on the flow of both the hot and cold media and the internal structure of the equipment. By making a CFD model it can be verified wether the full capacity of the heat exchanger is used or if non -uniform gas distribution leads to dead zones.
The starting point of a typical project is a detailed CFD study during which the characteristics of a heat exchanger design is evaluated:
- Velocity of the gas streams
- Heat transfer as a function of temperature and speeds
- Pressure drop over the length of the heat exchanger
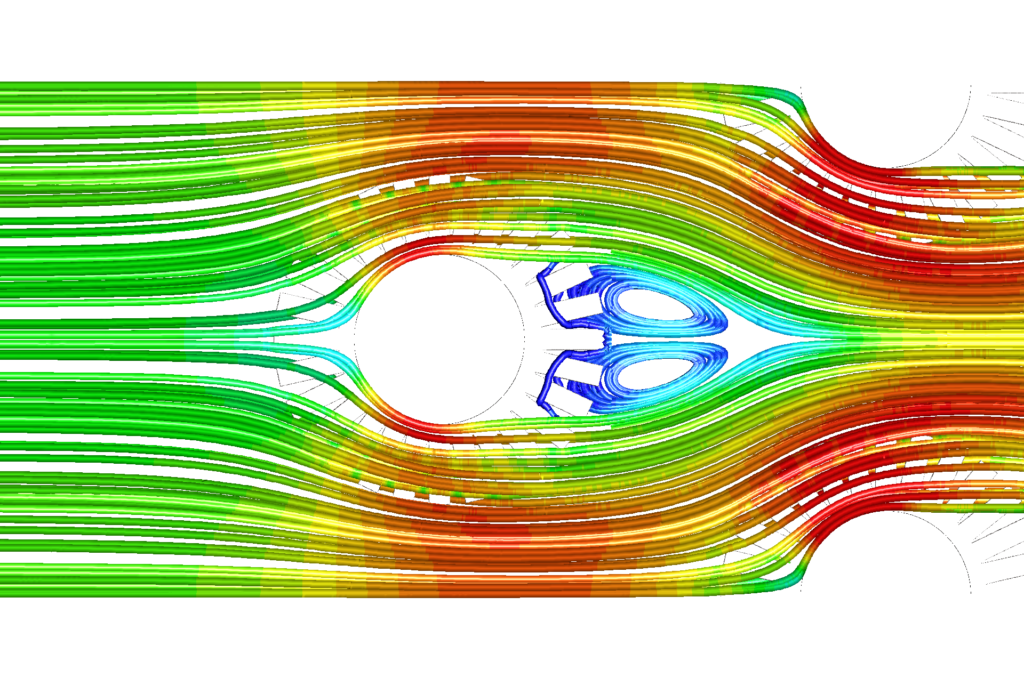
Streamlines 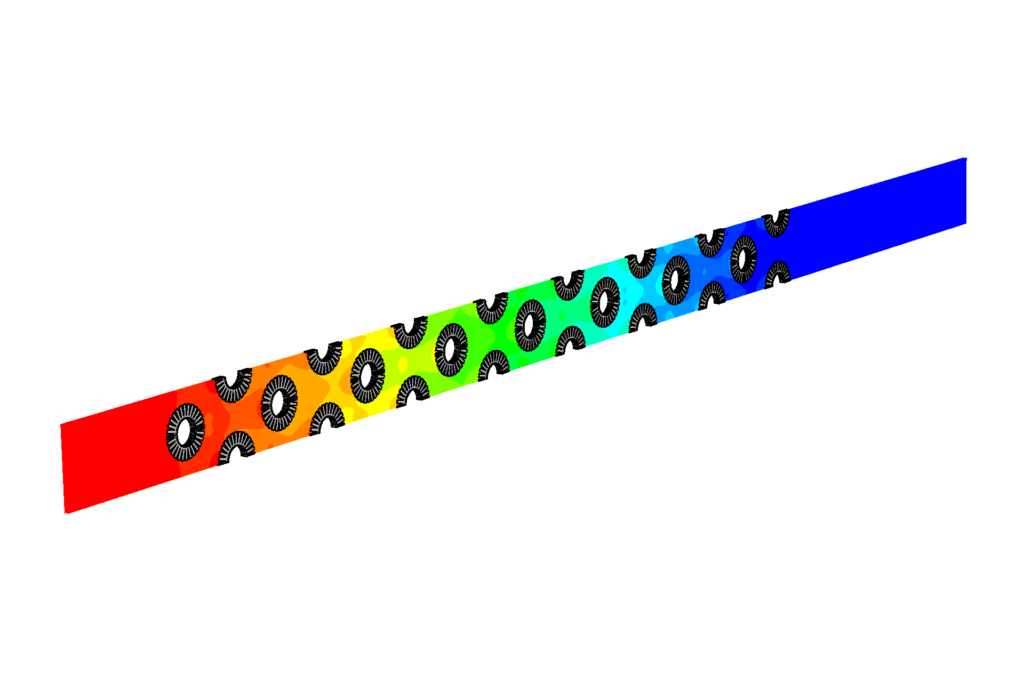
Pressure distribution 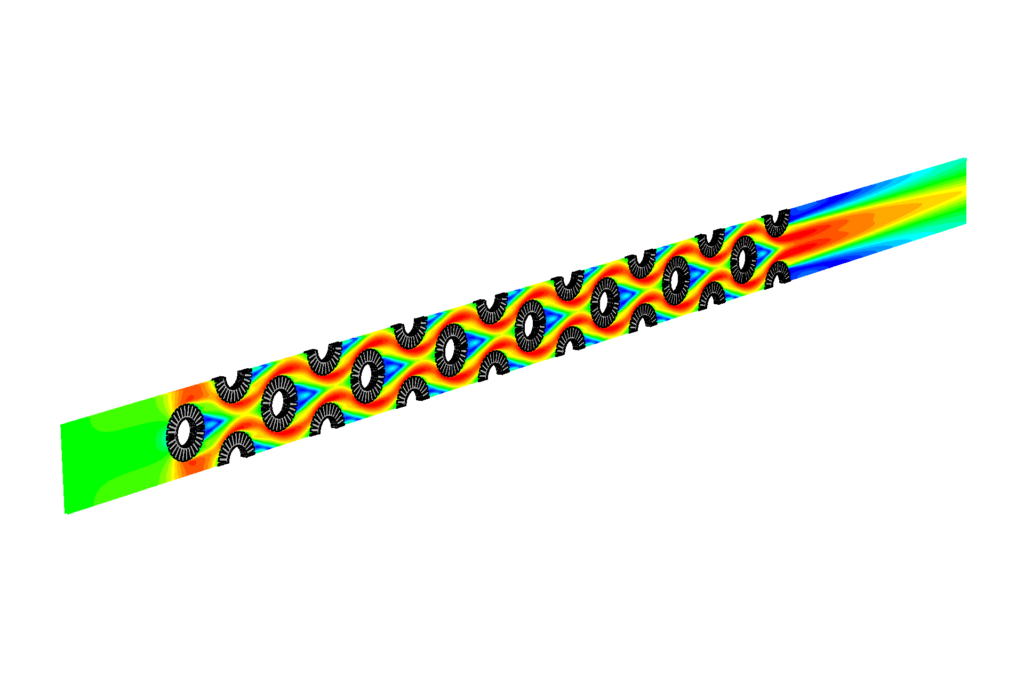
Gas velocity
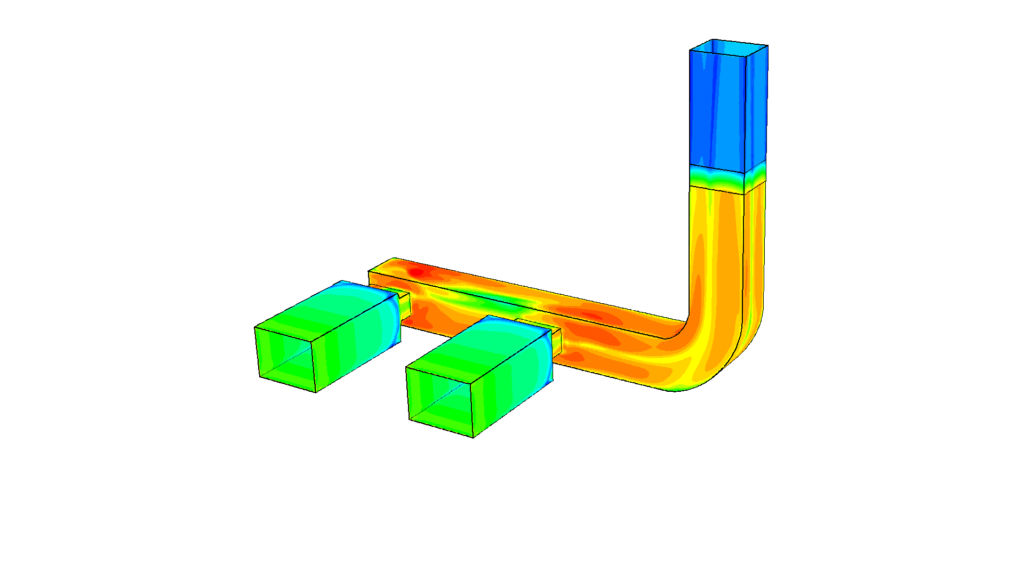
These characteristics are then used to verify the effect of the heat exchanger installed in a process. When a heat exchanger is installed in a gas stream it needs to be determined where in the ducts the gas flow uniformity is the best and what the effect on the overall pressure drop would be. The flow uniformity has a large impact on the heat exchange efficiency. The pressure drop induced by an obstruction in the gas stream influences the fan energy consumption.
As the calculations include an evaluation of the temperature of the gas stream also condensation problems can be studied. Condensation in the ducts might lead to corrosion issues or build up of accretions leading to fouling.
Temperature distribution 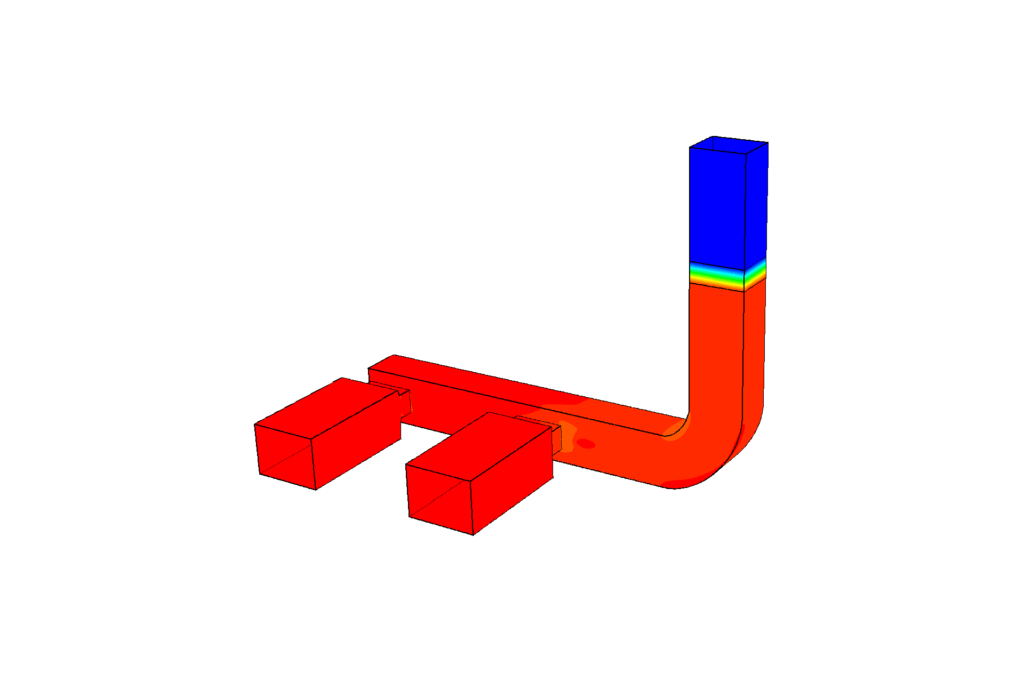
Pressure distribution
The same modelling technique can also be used to investigate the efficiency of cooling plates. The boiling refrigerant increases the complexity of the modelling work, but we at InsPyro do like a challenge. Our multidisciplinary teams combines the modelling power of CFD experts with knowledge on material behaviour.
